Heidelberg, Germany

The following description is courtesy of LAVA
A new energy storage tower for Stadtwerke Heidelberg (SWH) in Heidelberg, Germany has broken ground.
“LAVA’s design will transform the new water tank, a cylindrical-shaped storage centre, into a dynamic sculpture, a city icon, a knowledge hub on sustainable energy, fully accessible to the public, a strong symbol of the transition towards renewables,” said Tobias Wallisser, director of LAVA.
Stadtwerke Heidelberg (SWH) operates an extensive regional heating network and is building the new heating storage Tower and Park due for completion by mid 2019. Energy created by solar and wind will be used to heat up the water and sell it as heat energy.

“This ‘knowledge store’ will replace a previous gas tank, a symbol of energy policy in the 1950s. Formally and geometrically the new water tank will not be much different from its predecessor. So this raised the challenge for us: How can the parameters of energy regeneration, decentrality, networking, flexibility and adaptivity be made visible in the design of the outer shell? How can an adaptive, dynamic system be produced without extreme technical control? Our task was to transform a big heavy industrial tank into a dynamic object,” added Mr Wallisser.
“Since we won the competition a lot of engineering (wind tunnel testing, solar analysis and structural testing) has been executed to ensure that the design is optimised in regards to views, material distribution, solar gains and comfort level on the terraces.”
Tower

The transformation of the tank involves a multi-layered facade structure inspired by the geometries of nature. An inner shell, an insulating layer of mineral wool panels of different shades of blue, wraps the building. A spiral helix staircase positioned around the cylinder continues the “energy loops” circling the structure rising dramatically up the facade to the top.
A cable network arranged between the annular supports forms the outer façade layer and gives depth and a varied, dynamic appearance. Approximately 11,000 diamond-shaped plates of stainless steel are hooked with an ingenious connection to this steel network, allowing them to rotate horizontally up to 45 degrees in the wind. “This number of plates matches the number of households supplied with energy by the network,” said Wallisser, “a visual signifier of the impact new technology can make.”
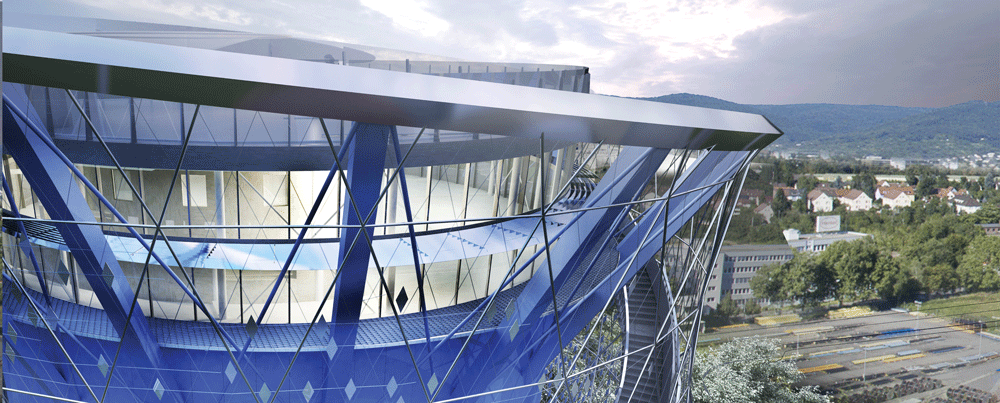
This dynamic envelope glimmers in sunlight, while gentle waves of light and motion glide across the surface. The complex interplay of movement, light and shadow is generated by sun and wind, with no additional energy or complicated technology required. At night, the inner envelope is illuminated dynamically by low-energy LED luminaires in blue, green and white, mounted below the stairs.
This colour play also signals the filling up or emptying of the water storage tank, making clearly visible the processes inside the tower.
Two elevators take visitors to the roof-level event spaces, bistro and terraces offering panoramic views.
Park

It was also important to bring all the elements of the site into one coherent plan. LAVA chose differently sized annular elements in different orientations, differently inclined ‘energy loops’, which continue from the park landscape to the façade of the store. And every element is multifunctional – the park becomes a three- dimensional structure, the energy storage becomes a view and experience space, escape stairs are vertical knowledge promenades, and elevators are a journey with a view of the city.
“As the tallest building in

“We teamed up with some of the best engineers for the project, Schlaich Bergermann for structure (responsible for sports stadia around the globe and the famous 1972 Munich Olympic Venue); Transsolar for climate engineering; and WHITEvoid for the kinetic façade (known for their light wall installation for the 25th anniversary of the fall of the Berlin wall).”
The project is shortlisted at WAF 2017 for ‘Future Infrastructure Projects’.

Details
Name of project: Energy Storage Centre
Location: Heidelberg, Germany
Client: Stadtwerke Heidelberg (SWH)
Status: Breaking ground 2017; completion due
Size:Diameter 25m; Height 56m; Capacity 19,500m3/40MW); Total park site 10.000m2
Practice Credits
General Planners: LAVA and Wenzel+Wenzel
Architecture: LAVA (Tobias Wallisser, Alexander Rieck, Chris Bosse with Christian Tschersich, Christina Ciardullo, Courtney Jones,
Structure: Schlaich Bergermann sbp, Stuttgart (Knut Stockhusen, Rudolf Bergermann, Jörg Mühlberger, Daniel Gebreiter)
Landscape Design: A24 Landschaft Berlin (Steffan Robel, Maren Jeschke, Daniel Angulo-Garcia
Climate engineering: Transsolar, Stuttgart
Kinetic facade: WHITEvoid, Berlin
Facades: Priedemann GmbH, Berlin
MEP: IBH, Frankfurt
Building physics: CAPE, Esslingen
Image credits: LAVA, sbp, A24, WHITEvoid




